The model we have created does not capture situations where the product is consumed, discarded, or upgraded, all of which lead to repeat purchases. We will model repeat purchase behavior by assuming that adopters move back into the population of potential adopters when their first unit is discarded or consumed.
First, we will define a constant representing the average lifetime of product.
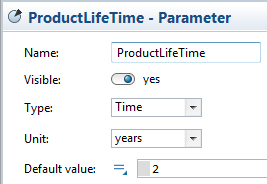
Create the ProductLifeTime constant
- Assume that the average duration of active use of our product is 2 years. Type 2 as the Default value.
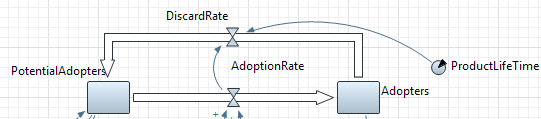
People move back from the adopter population to the pool of potential adopters when the product they have purchased is discarded or consumed. So, the discard flow is nothing else but the adoption flow delayed on the average lifetime of the product.
Create the discard flow from Adopters to PotentialAdopters
- Now we want to add a flow going from
 Adopters to
Adopters to
 PotentialAdopters. But if we will draw it with a straight arrow, it will overlap
PotentialAdopters. But if we will draw it with a straight arrow, it will overlap
 AdoptionRate flow on the diagram. That’s why we need to create a flow of a custom shape, like shown in the figure given below.
AdoptionRate flow on the diagram. That’s why we need to create a flow of a custom shape, like shown in the figure given below. - To draw a flow of a custom shape, double-click the element in the
 System Dynamics palette so that its icon turns into
System Dynamics palette so that its icon turns into  .
. - Right after that, go to the graphical editor and click the stock where the flow flows out (
 Adopters).
Adopters). - Then click in the intermediate salient points.
- Finally, click the
 PotentialAdopters stock. New flow from
PotentialAdopters stock. New flow from
 Adopters to
Adopters to
 PotentialAdopters is added.
PotentialAdopters is added. - Change the name of the flow to DiscardRate.
- You can see that stock formulas have changed as well:
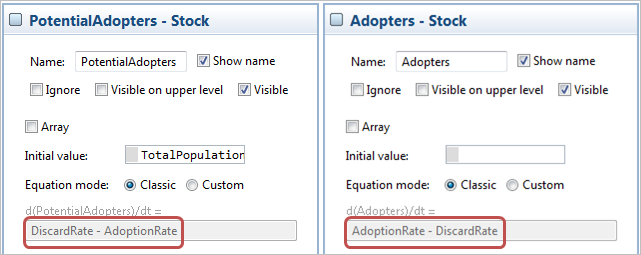
- Set the following formula for the flow variable: delay(AdoptionRate, ProductLifeTime)
The delay() function implements the time delay and has the following notation: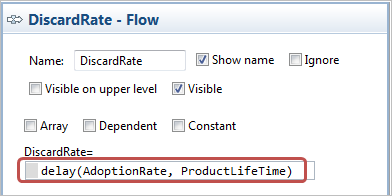
delay(<variable>, <delay value>, <initial value>)
In our case, the function reproduces AdoptionRate delayed on the
AdoptionRate delayed on the
 ProductLifeTime value. The discard rate is null until the time of use of the first purchased products elapses.
ProductLifeTime value. The discard rate is null until the time of use of the first purchased products elapses.
Set DiscardRate to be displayed by the lower time plot
- Just add DiscardRate as one more data item to be displayed by this plot (adding items onto plots is described in the previous phase).
- Specify Discard rate as the title of this data item.
Now we have finished modeling the product replacement purchases. You may check how the delay() function works. Run the model and view plots for
 AdoptionRate and
AdoptionRate and
 DiscardRate. You can see that rate curves look exactly how we expected — the discard rate is actually the adoption rate delayed by 2 years — the lifetime of the product.
DiscardRate. You can see that rate curves look exactly how we expected — the discard rate is actually the adoption rate delayed by 2 years — the lifetime of the product.
Observe the population dynamics using the chart. Now, instead of falling to zero, the potential adopter population is constantly replenished as adopters discard the product and re-enter the market. The adoption rate rises, peaks, and falls to a rate that depends on the average life of the product and the parameters determining the adoption rate. Discards mean there is always some fraction of the population in the potential adopter pool.
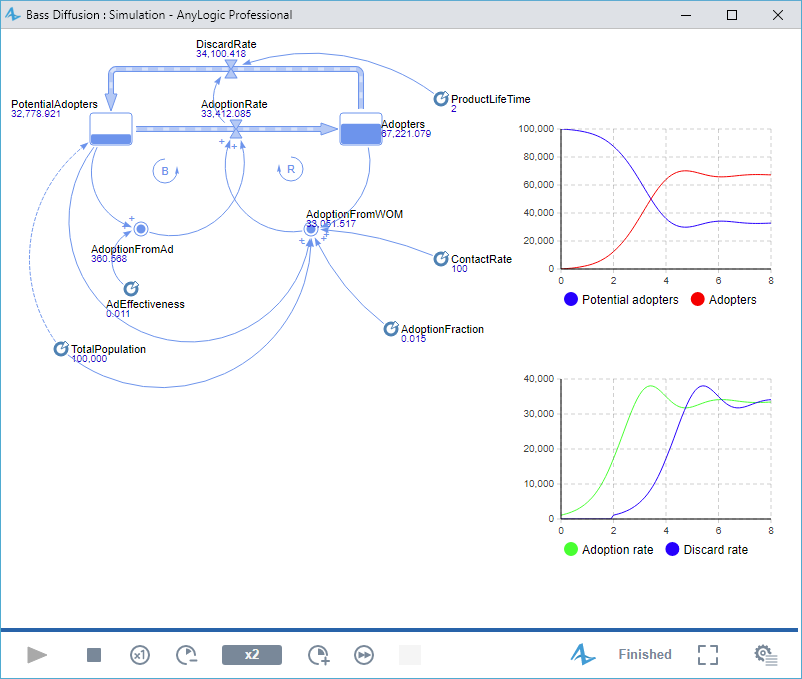
If you like, you may add control group varying product lifetime, say from 0.5 to 10.
Demo model: Bass Diffusion — Phase 3 Open the model page in AnyLogic Cloud. There you can run the model or download it (by clicking Model source files). Demo model: Bass Diffusion — Phase 3Open the model in your AnyLogic desktop installation.-
How can we improve this article?
-

