In the first phase, we created the model simulating a simple pedestrian flow: passengers enter the subway entrance building and go to the trains walking through the hall.
Now we want passengers to pass through the fare gates before entering the subway platform. So let’s add fare gates at the end of the corridor.
Fare gates are a typical example of services used in pedestrian models.
There are two types of space markup shapes you may use to draw services in your pedestrian model:
-
 Service With Lines — Used to define services where pedestrians wait in queue lines until the service becomes
available.
Service With Lines — Used to define services where pedestrians wait in queue lines until the service becomes
available. -
 Service With Area — Used to define services with electronic queue. Pedestrians in this case do not stand in
lines, but wait in the neighboring area.
Service With Area — Used to define services with electronic queue. Pedestrians in this case do not stand in
lines, but wait in the neighboring area.
Fare gates are naturally represented by Service with Lines.
Draw the fare gates
- Drag the
 Service With Lines element from the Space Markup section of the
Service With Lines element from the Space Markup section of the
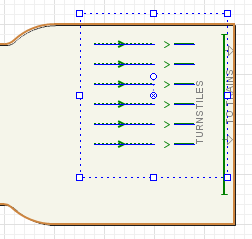
 Pedestrian Library palette into the graphical editor. You will see two service points and two queue lines leading to these points. Place the shapes as shown in the figure below:
Pedestrian Library palette into the graphical editor. You will see two service points and two queue lines leading to these points. Place the shapes as shown in the figure below:
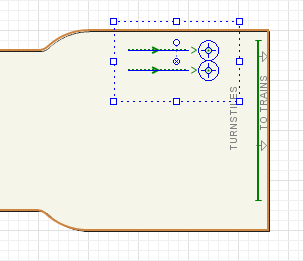
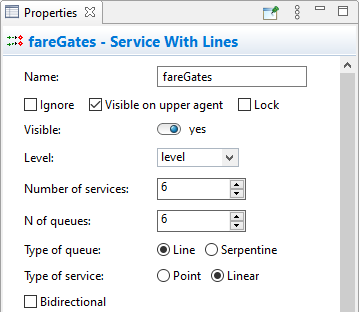
- Configure the services. Name it fareGates.
- It’s evident that two fare gates are not enough. Increase the Number of services to 6 and change the N of queues to 6 also.
- Change the Type of service from Point to Linear.
There are two types of services:
- Linear service defines a line, along which pedestrians should move. Pedestrian services at beginning point of the line and then moves to the end point before leaving the service. fare gates are naturally linear services.
- Point service defines a point, where pedestrians should stay on for service delay time. Pedestrian reaches the service point and starts waiting there for the specified delay.
You will see that the service points became lines:
Now we will modify the model flowchart.
Modify the model flowchart
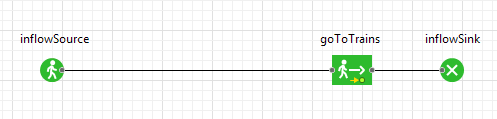
- Prepare the place for the new block in our flowchart. Move goToTrains and inflowSink blocks to the right as shown below:
-
Now we can insert a
 PedService block in our flowchart.
PedService block in our flowchart.
 PedService simulates how pedestrians go to the services defined graphically with the markup shape
and get serviced there. Drag
PedService simulates how pedestrians go to the services defined graphically with the markup shape
and get serviced there. Drag
 PedService block from the
PedService block from the
 Pedestrian Library palette onto the graphical diagram, right after the pedestrian source block. Placing the block right onto the connector, we connect the ports automatically.
The right port of the
Pedestrian Library palette onto the graphical diagram, right after the pedestrian source block. Placing the block right onto the connector, we connect the ports automatically.
The right port of the PedService block should get connected, not the lower port.
PedService block should get connected, not the lower port.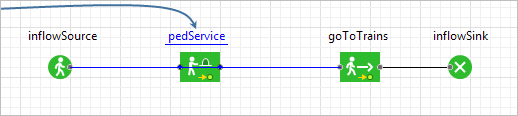
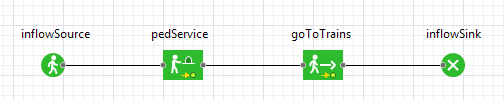
- Now
 PedService will appear in the flowchart, connected automatically.
PedService will appear in the flowchart, connected automatically.
Configure the flowchart blocks
- Open the Properties of the
 PedService block.
PedService block. - Rename the block to atFareGates.
- Choose
 fareGates (the name of our
fareGates (the name of our
 Service With Lines markup shape) as the Services.
Service With Lines markup shape) as the Services. - You can see that the Delay time is uniformly distributed with minimum value of 2 seconds and maximum value of 3 seconds. Leave it since it is typical delay time for fare gates.
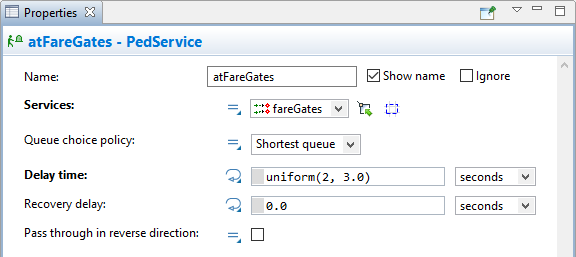
We have defined the new logic and now we can run the model and observe its behavior.
Build the model by clicking the
 Build model toolbar button. If there are some errors in your model, the
Build model toolbar button. If there are some errors in your model, the
 Problems view appears listing all the errors found in your model. Double-click an error in the list to open the location of the error and fix it.
Problems view appears listing all the errors found in your model. Double-click an error in the list to open the location of the error and fix it.
After the model is successfully built, you can start it. Running the simulation, you automatically bring the current model up to date.
Run the model
- Run the model. You can see that now passengers pass through fare gates and the lines get very long instantly. So we should increase the number of fare gates.
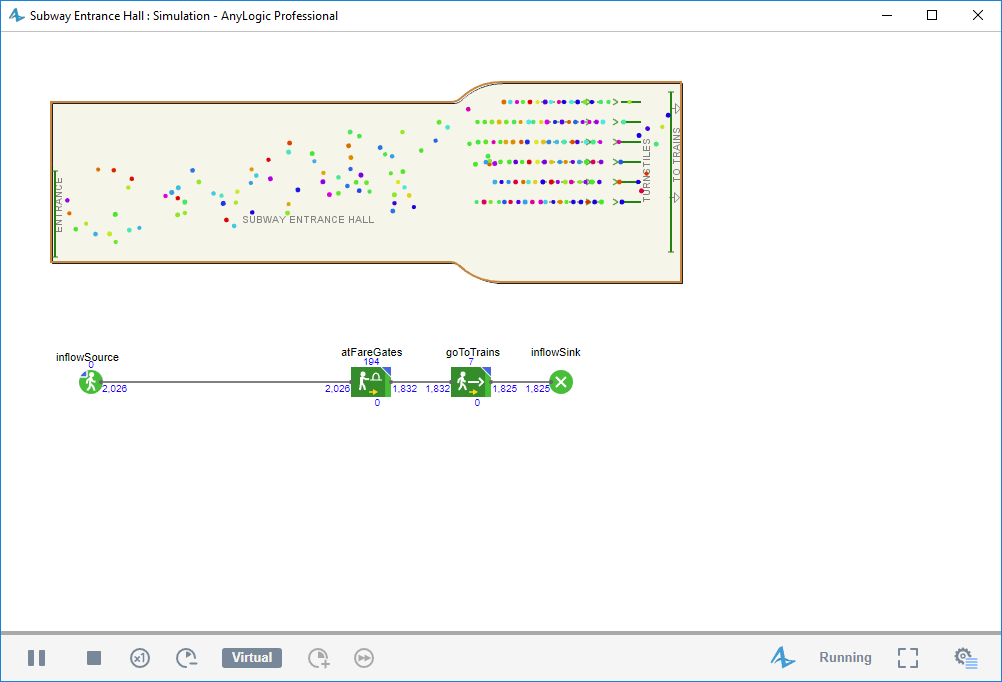 6 fare gates. Terrible lines.
6 fare gates. Terrible lines. - Stop the model and open the properties of the service shape again. Increase the number of services and number of queues to 7.
Run the model again and see how the things are going on now. You may think that everything is OK now. But actually we simulate the model rather slowly, to understand the global trend, we recommend you to run the model faster to get the answer whether the lines are growing or not.
You can adjust the execution speed using  Slow down and
Slow down and  Speed up controls. Right now, it is better to switch to virtual time mode to view simulation run at its maximum speed and simulate a long period of time. To enable virtual time mode click the Run as fast as possible (virtual time mode)
Speed up controls. Right now, it is better to switch to virtual time mode to view simulation run at its maximum speed and simulate a long period of time. To enable virtual time mode click the Run as fast as possible (virtual time mode)  control.
control.
Simulating a long period of time gives us the answer. Lines are still growing, not so fast as before, but sometimes they may become rather significant. So... 7 fare gates probably are still not enough to serve the flow of 4000 pedestrians per hour.
So let’s increase the number of fare gates once more. Please change the number of services and number of queues to 8 and run the model again.
Finally our configuration is acceptable — the station can cope with such pedestrian flow successfully.
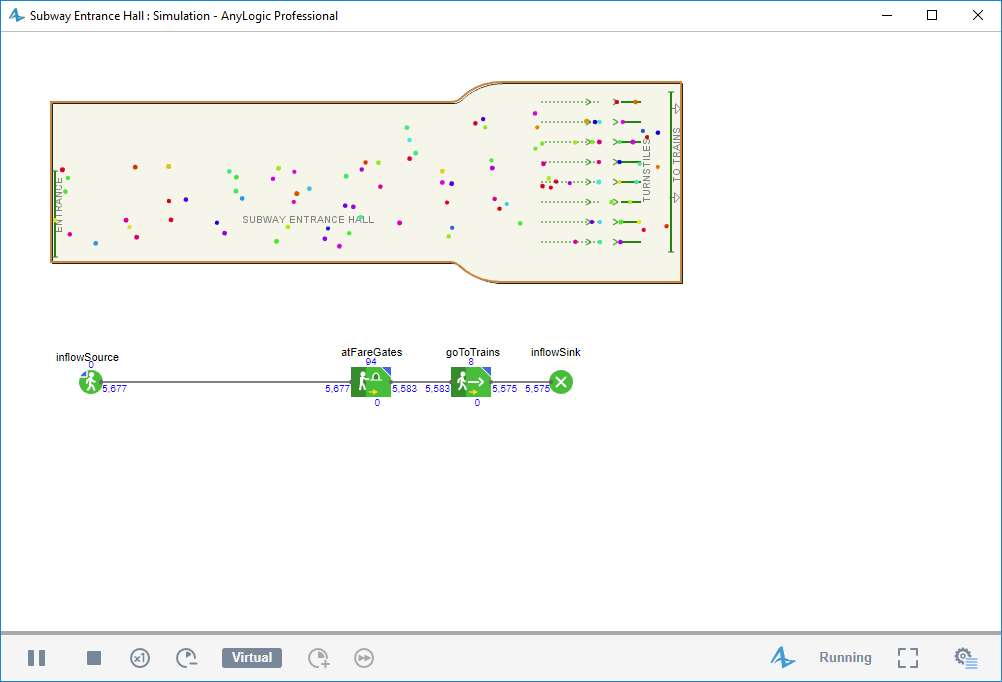 8 fare gates. Queues are reasonable.
8 fare gates. Queues are reasonable.
So we got the first practical use of our model. This model helped us to find the required number of the service points. You can play with pedestrian arrival rates in the settings of the
 PedSource block and analyze how to improve the facilities to cope with the load.
PedSource block and analyze how to improve the facilities to cope with the load.
Save the model by clicking  Save and keep doing this from time to time as you develop the model. Now we can continue.
Save and keep doing this from time to time as you develop the model. Now we can continue.
-
How can we improve this article?
-

