Applies to AnyLogic Cloud 2.7.0. Last modified on February 13, 2026.
When creating an optimization experiment (Optimization or Optimization with replications), you should set its Objective. The objective is a numerical value (int or double) that you want to minimize or maximize through the optimization experiment.
The Objective control is already available in the Inputs section when you create an experiment. You must select one of the experiment’s outputs from the drop-down list and specify whether you want to minimize or maximize it using the Minimize and Maximize radio buttons.
AnyLogic Cloud optimization experiments support requirements. A requirement is an additional restriction placed on the solution found by the optimization engine. These requirements are checked after each simulation run, and if they are not met, the used inputs are rejected. Otherwise, they are accepted.
By default, the requirements are hidden, but you can make them visible in the dashboard editor.
To configure a requirement
- Go to the dashboard editor.
- Locate the Requirements section below the experiment settings.
-
The Requirements section lists all the numeric (int and double) inputs of the model.
To create a requirement for a particular input, make it visible by clicking . - Save the dashboard.
- The Requirements block will appear in the Inputs section, displaying the name of the input you have selected, a drop-down list, and an edit box.
-
In the drop-down list, select the type of restriction you want to apply to the input:
- Not restricted
- Greater than or equal to
- Less than or equal to
- In range
- In the edit box, specify the value (or range) that will serve as the limit for the corresponding input.
Now, when the optimization process is complete, if the requirement is not satisfied during the simulation run, the optimization engine will consider the solution for that run infeasible, and the objective will remain unfulfilled.
Starting from version 2.7.0, Cloud optimization experiments also support constraints.
A constraint is a more complex condition defined upon optimization parameters, which is tested each time the optimization engine generates a new set of values. It is used in cases when the value of a decision variable must be described more precisely than simply a range.
Usually, a constraint is a well-formed arithmetic expression describing a relationship between the optimization parameters:
parameterA + parameterB + 2 * parameterC = 10
parameterC - parameterA * parameterB >= 300By default, an optimization experiment has no constraints.
To configure constraints
- Go to the dashboard editor.
- Locate the Constraints section below the experiment settings.
-
Click + Add constraint.
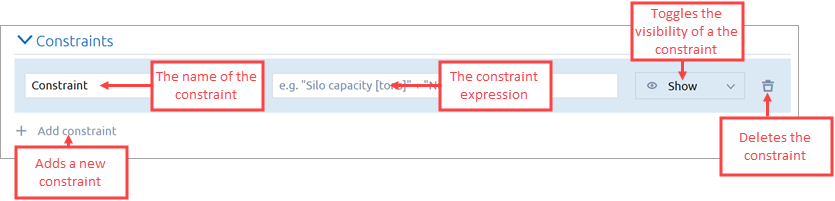
- In the first edit box, specify the name of the constraint. This name will be visible on the dashboard when changing the input values.
-
In the second edit box, specify the arithmetic expression that will serve as a constraint. See some examples above.
Within the edit box, you can use input values (specified by their names in quotation marks) and some built-in functions.
Note that the expression used to calculate the constraint is not visible on the dashboard. To view it, you need to edit the dashboard. -
Add more constraints as you need, one by one.
-
Save the dashboard.
AnyLogic checks for the validity of constraint expressions and identifies issues, if there are any. - If everything is correct, then when you save the dashboard, the Constraints block will appear in the Inputs section, displaying the name of the constraint that you have specified, a drop-down list, and an edit box.
-
In the drop-down list, select the type of restriction you want to apply to the constraint:
- Not restricted
- Greater than or equal to
- Less than or equal to
- In range
- In the edit box, specify the value (or range) that will serve as the limit for the corresponding constraint.
When running the constraint-restricted experiment, AnyLogic calculates the validity of the constraint expression. If there is an issue, the run is not started at all, and the optimization engine does not consider this run as an iteration.
Custom constraints support a set of built-in mathematical constants and functions that can be used in expressions. Use them to perform common operations when defining constraints.
- Constants
-
When specifying constants, use them without quotation marks (for example, pi, not "pi"). Quoted values are interpreted as names of model inputs.
Constant Description pi The value of π as defined in Math.PI in Java. e The value of Euler’s number ⅇ. - Functions
-
Function Description abs Returns the absolute value of a number (the distance from zero). For example, abs(-5) returns 5. acos Returns the angle (in radians) whose cosine is the given value. asin Returns the angle (in radians) whose sine is the given value. atan Returns the angle (in radians) whose tangent is the given value. cbrt Returns the cubic root of a number. For example, cbrt(8) returns 2. ceil Rounds a number up to the nearest integer. For example, ceil(2.3) returns 3. cos Returns the cosine of an angle (in radians). cosh Returns the hyperbolic cosine of a value. exp Returns Euler’s number (e) raised to the given power. floor Rounds a number down to the nearest integer. For example, floor(2.9) returns 2. log Returns the natural logarithm (base e) of a number. log10 Returns the logarithm (base 10) of a number. log2 Returns the logarithm (base 2) of a number. sin Returns the sine of an angle (in radians). sinh Returns the hyperbolic sine of a value. sqrt Returns the square root of a number. For example, sqrt(9) returns 3. tan Returns the tangent of an angle (in radians). tanh Returns the hyperbolic tangent of a value. signum Returns the sign of a number: -1 for negative values, 0 for zero, and 1 for positive values.
-
How can we improve this article?
-

