Option list is the element for defining agent attributes that have limited choice of alternative options, e.g.:
- Gender (male, female)
- Marital status (single, married, separated, divorced, widow)
For example, you can define the agent’s gender attribute as a Gender option list with the following elements: Male, Female.
To create an option list
-
In the Projects view, right-click (macOS: Ctrl + click) the model you are currently working with and choose New >
 Option List… from the context menu.
Option List… from the context menu.
- The New Option List dialog box opens. In the Name box, specify the name of the new option list. In our example the name is Gender.
-
In the Specify elements table, type the names of the options (Male and Female).
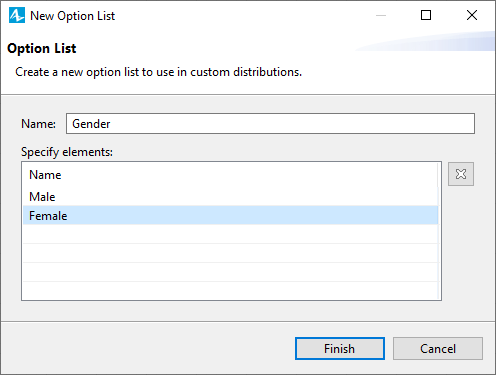
- Click Finish to complete the process.
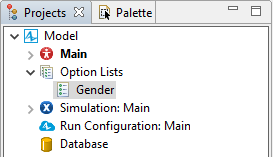
In the project tree, option lists appear on the upper level, grouped in the  Option Lists branch.
Option Lists branch.
Having defined the option list, you can choose this list as the agent parameter’s type.
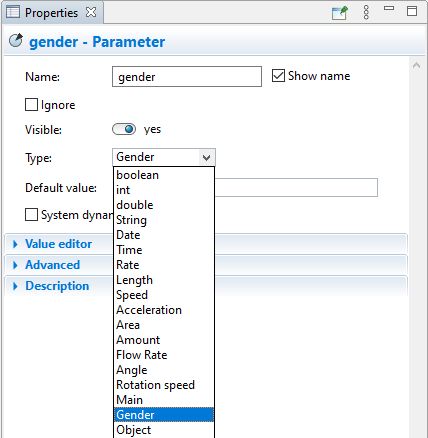
Now you can assign values (Male or Female) to the agent’s gender parameter.
To set a default value, specify an option list’s value in the parameter’s Default value field, e.g: Male.
To change the value at the model runtime, type gender = Female;
If you need to assign values for the whole agent population, you may do it e.g. in the top level agent’s Startup code.
For example, you have the option list named Gender. To randomly select one option from this option list, use one of the following functions:
- randomFrom( Gender.class );
- Gender.random( this );
In the Java code of the model, an option list is a representation of the standard Java Enum class. It means you can use the standard Java API to interact with the option list in your code and perform basic tasks.
For example, suppose you have an option list SpeedMode with the following values: Slow, Normal, Fast.
To get all items in the option list, use the values() function:
SpeedMode[] allModes = SpeedMode.values();
After executing this code, the allModes array will be [Slow, Normal, Fast]. This is useful when you want to loop through all options or count them. Here are some examples:
-
To iterate over all items, use a simple loop on the values() array:
for (SpeedMode m : SpeedMode.values()) { traceln(m); // prints Slow, Normal, Fast } -
To count how many items there are in the list, use length:
int count = SpeedMode.values().length; // the count value is 3
For individual items of the option list, you can use additional functions:
-
To return the exact identifier of an item as it is declared in the option list, use name():
SpeedMode m = SpeedMode.Normal; String id = m.name(); // "Normal" traceln("Selected: " + id); -
To return the position of the item in the option list, use ordinal():
SpeedMode m = SpeedMode.Fast; int index = m.ordinal(); // 2 (the function is zero-based) -
To convert a string to an option list item, use valueOf():
This is particularly useful when reading data from external resources, such as files, databases, or user input, where values are stored as strings. Note that the function is case-sensitive.String speedText = "Fast"; SpeedMode m = SpeedMode.valueOf(speedText); // returns SpeedMode.Fast
For a full list of available Enum functions, see the Java 17 documentation.
-
How can we improve this article?
-

