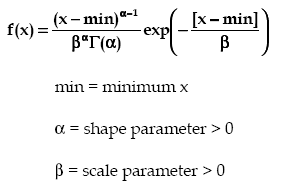
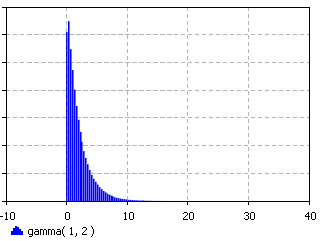
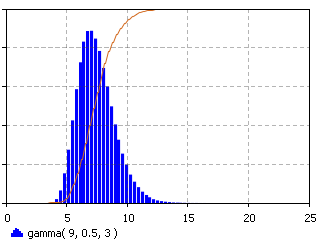
The Gamma distribution is a continuous distribution bounded at the lower side. It has three distinct regions. For alpha = 1, beta = 1/lambda the Gamma distribution reduces to the exponential(lambda) distribution, starting at a finite value at minimum x and decreasing monotonically thereafter. For alpha < 1, the Gamma distribution tends to infinity at minimum x and decreases monotonically as x increases. For alpha > 1, the Gamma distribution is 0 at minimum x, peaks at a value that depends on both alpha and beta, decreasing monotonically thereafter. If alpha is restricted to positive integers, the Gamma distribution is reduced to the Erlang distribution.
The Gamma distribution can also be used to approximate the Normal distribution, for large alpha, while maintaining its strictly positive values of (actually, (x - min)).
The Gamma distribution has been used to represent lifetimes, lead times, personal income data, a population about a stable equilibrium, interarrival times, and service times. In particular, it can represent lifetime with redundancy.
Examples of each of the regions of the Gamma distribution are shown above. Note the peak of the distribution moving away from the minimum value for increasing alpha, but with a much broader distribution.
- Description
- Generates a sample of the Gamma distribution.
- Parameters
-
Name Type of value Description alpha double The shape parameter > 0. beta double The scale parameter > 0. min double The minimum x value. - Result
-
Type Description double The generated sample.
- Description
- Generates a sample of the Gamma distribution with min set to 0. Is equivalent to gamma(alpha, beta, 0).
- Parameters
-
Name Type of value Description alpha double The shape parameter > 0 beta double The scale parameter > 0. - Result
-
Type Description double The generated sample.
- Description
- Generates a sample of the Gamma distribution using the specified random number generator.
- Parameters
-
Name Type of value Description alpha double The shape parameter > 0. beta double The scale parameter > 0. min double The minimum x value. r java.util.Random The random number generator. - Result
-
Type Description double The generated sample.
This document includes content from the “Stat::Fit User’s Manual”. Copyright 2016 Geer Mountain Software Corp.
-
How can we improve this article?
-


