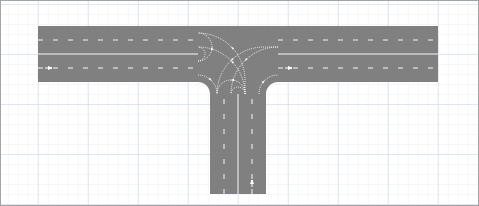
The Intersection is a graphical space markup element that is used to connect two or more roads. Roads, intersections, and other space markup elements are used to draw road networks for Road Traffic Library models.
The intersection controls the direction of traffic using lane connectors, which indicate routes for cars on each road lane as vehicles cross the intersection.
Let us demonstrate how to draw an intersection using the example of the intersection of Wilhelmstraße and Behrenstraße in Berlin, near the Brandenburg Gate:

The scenario is typical for all types of intersections. Steps 1-3 show how to draw a T-shaped intersection, then we continue and end up with a four-way intersection.
To draw an intersection
-
First, draw Wilhelmstraße. You draw a linear road by clicking
Road in the
 Road Traffic Library palette, then adding the starting point of the road with a mouse click, and finally placing the final point of the road with a double click.
Road Traffic Library palette, then adding the starting point of the road with a mouse click, and finally placing the final point of the road with a double click.
Both roads are two-way, so it does not matter in which direction you will draw this road. To learn how to draw a road in more detail, complete the short tutorial described in Road.
-
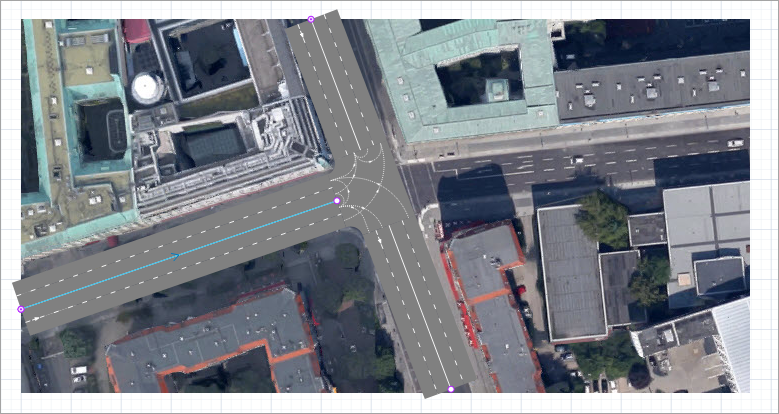
Now let’s draw Behrenstraße leading from the left to the intersection. Start drawing the road by clicking its median strip on the left edge of the map. The next step is to set the end point of the road we are drawing. If you move the mouse over certain points of Wilhelmstraße, you will see purple points indicating the possible connection points. To properly connect the roads and get a T-shaped intersection, click the median of Wilhelmstraße (see the figure below).

-
The three-way intersection will be drawn. Each road connected to the intersection gets a stop line on the lane with traffic moving towards the intersection. This is a regular AnyLogic stop line that you can edit. You will also see a number of lane connectors drawn at the intersection. They define the allowed traffic directions at the intersection. By default they are typical for an intersection, so there is no need to edit them in our case.
-
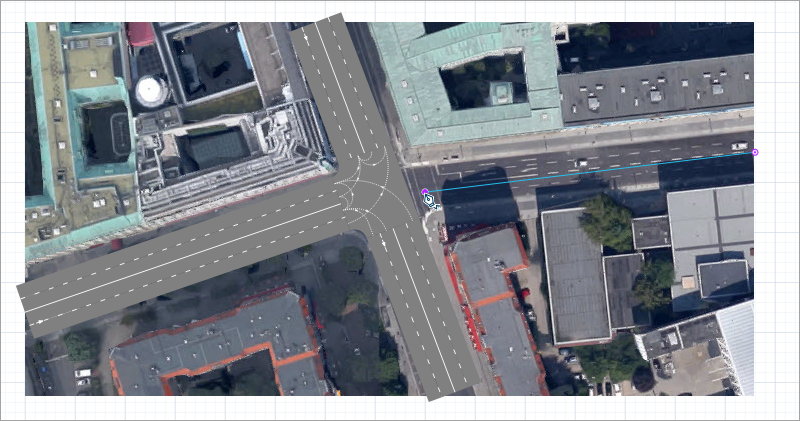
Now draw Behrenstraße, which enters the intersection from the right. This time you should place the road end point close enough to Wilhelmstraße so that you can see the purple point, as shown in the figure below.
-
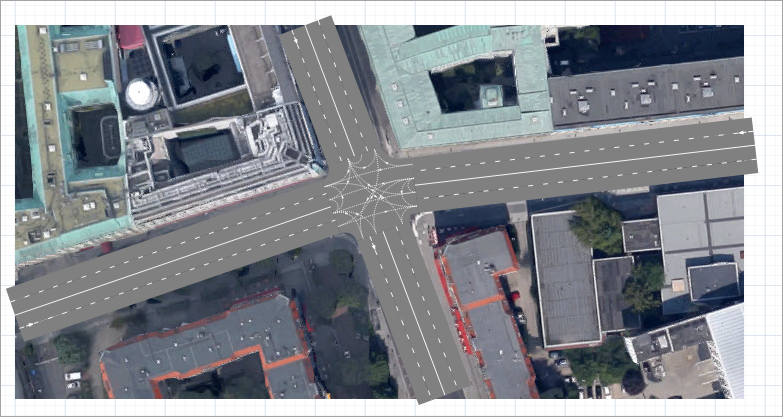
A four-way intersection will be drawn. Check that it has the correct lane connectors and stop lines, as shown in the figure below. If it looks different, try redoing some of the previous steps.
- General
-
Name — The name of the intersection. The name is used to identify and access the intersection shape from code.
Show name — If selected, the shape name is displayed in the graphical editor.
Lock — If selected, the intersection is locked. Locked elements do not respond to mouse clicks, and they cannot be selected in the graphical editor until you unlock them. This is often needed when you want to prevent the element from being edited while other elements are placed over it.
Ignore — If selected, the intersection is excluded from the model.
- Visibility and presentation
-
Visible — If selected, the road is visible during animation at model runtime.
Show in — Select whether the shape is displayed in both 2D and 3D animation, 2D only, or 3D only.
Agent presentation — If selected, the road is also visible on the upper-level agent that hosts the agent containing this road.
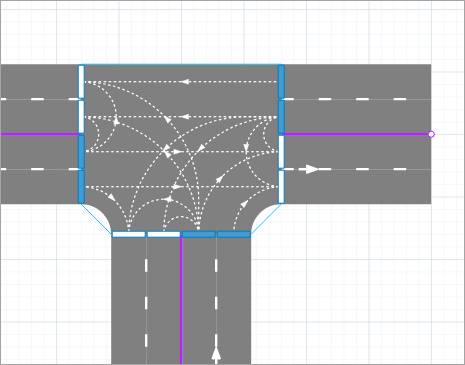
Lane connectors define the allowed directions of traffic at an intersection. To enable car movement from one lane to a specific lane on another road, enable the lane connector that connects the respective lane ends.
By default, AnyLogic activates the connectors that are typical for the intersection of the current topology.
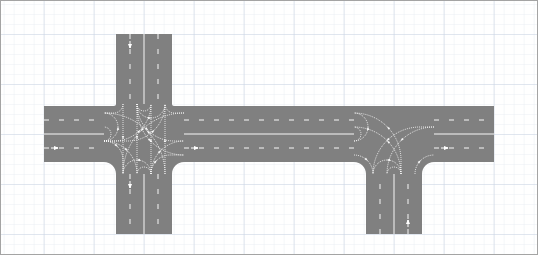 Default lane connectors for the four-way and T-shaped intersections
Default lane connectors for the four-way and T-shaped intersections
Cars strictly follow lane connectors as they travel through the intersection.
If you need to customize traffic directions on the intersection, you can disable existing connectors, draw additional connectors, and change connector shapes.
To disable an existing lane connector
- Click the intersection to select it. The selected intersection highlights the lane handles, one for each lane.
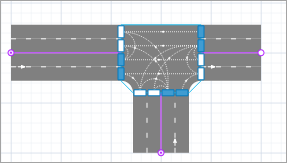
- Click the lane connector to select it.
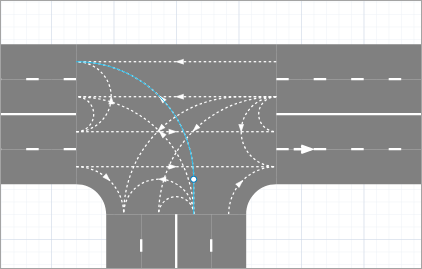
- Press Delete. The lane connector will be removed and movement in that direction will be prohibited.
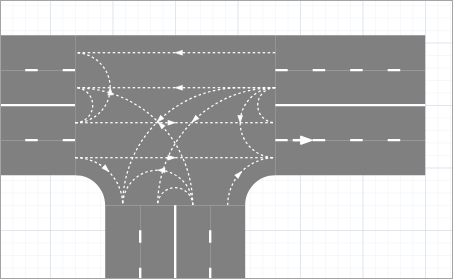
To draw more lane connectors
Let us show how to make traffic flow from the lower road to the right road.
-
Click the intersection to select it. The selected intersection highlights the lane handles, one for each lane.

-
Click the lane handle corresponding to the lane to which you want to add connectors. You will enter the lane connector editing mode, which contains all enabled (shown as solid lines) and disabled (shown as dashed lines) lane connectors leading to or from the current lane, depending on the direction of traffic.
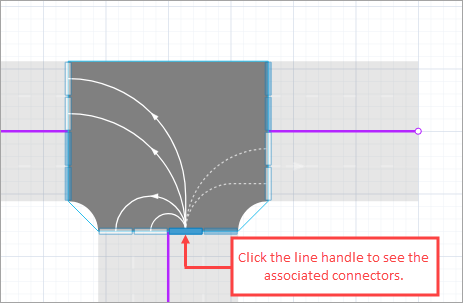
-
Click the disabled lane connector to activate it. When it becomes solid, it becomes active. This allows you to enable or disable traffic directions from the selected lane.

-
Click anywhere in the graphical editor to exit the lane connector edit mode. You will see the changes you just made.
If the default connectors created by AnyLogic are similar to the ones you need, you can modify them slightly. However, if they differ drastically, it may be easier to draw all the required lane connectors from scratch. In this case you should start with deleting all the existing lane connectors.
To delete all lane connectors
- Right-click the intersection and select Remove lane connectors from the context menu. Be careful not to right-click any of the lane connectors at this intersection, as this will open the lane connector context menu with other commands.
To reset lane connectors to default
- Right-click the intersection and select Reset lane connectors from the context menu. Be careful not to right-click any lane connector of this intersection, as this will invoke lane connector context menu with other commands.
To alter the lane connector shape
- Click the intersection to select it.
-
Click the lane connector you want to edit.
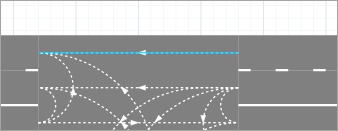
-
You may see a round point on the connector’s shape if it is long enough. This is the connector’s salient point. The smaller connectors do not have salient points by default. If you need a connector with a complex shape, add another salient point.
To add a salient point, double-click the lane connector anywhere. -
Move the salient point by dragging. You will see the shape of the connector change.
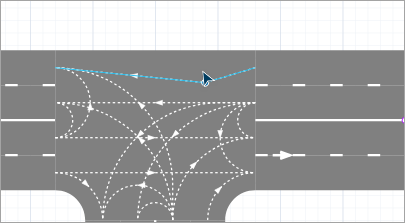
- When done, release the mouse button. Cars using this lane connector will follow its new shape as they pass through the intersection.
- Click anywhere in the graphical editor to remove the selection from the lane connector.
To make a lane connector linear or curved
- Click the intersection to select it.
- Right-click the desired lane connector and select Make segment line or Make segment curve from the context menu.
- You can change the shape of other segments as needed. When you are finished, click anywhere on the graphical diagram to exit this editing mode.
- Cars
-
Function Description int nCars() Returns the number of cars located on this intersection. List<Agent> getCars() Returns the unordered list of cars located on this intersection. - Lane connector statistics
-
Function Description int traffic() Returns the number of cars that have passed through this lane connector during 1 hour of model time. To obtain this result, we count the cars that have passed through this intersection during the last 5 minutes of model time and multiply that number by 12. int countCars() Returns the total number of cars that have passed through this lane connector since the start of the model run. void resetStats() Resets the counters for the countCars() and traffic() functions of the lane connector. - Intersection statistics
-
Function Description int traffic(Road from, Road to) Returns the number of cars that have passed between the specified lanes during 1 hour of model time. This result is the sum of traffic() for each lane connector between the specified lanes.
from — a lane connected to the intersection
to — a lane connected to the intersectionint countCars(Road from, Road to) Returns the number of cars that have passed between the specified lanes since the start of the model run. The result is the sum of countCars() for each lane connector between the specified lanes.
from — a lane connected to the intersection
to — a lane connected to the intersectionvoid resetStats() Resets the counters for the countCars() and traffic() functions of the intersection. - Visibility
-
Function Description void setVisible(boolean v) Sets the visibility of the intersection.
v — the visibility of the intersection: if true — the intersection is visible, if false — not visible.boolean isVisible() Returns the visibility of the intersection. If it returns true, the intersection is visible, if false — not void showLaneConnectors(boolean showLaneConnectors) Returns the visibility of lane connectors of the intersection.
showLaneConnectors — the visibility of lane connectors: if true — the connectors are visible, if false — not visible. - Advanced
-
Function Description RoadNetwork getRoadNetwork() Returns the road network to which this intersection belongs. List<RoadLanesConnector> getLanesConnectors() Returns the list of lane connectors inside this intersection. - Level
-
Function Description Level getLevel() Returns the level on which this intersection is located. - Removal
-
Function Description void remove() Removes the intersection from the presentation. If the intersection is not a part of presentation, the function does nothing. Removal from the presentation does not necessarily mean removal from the model logic: logical networks and routes may have been created prior to removal and survive.
-
How can we improve this article?
-


