| Density |
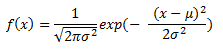
|
| Mean |
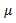
|
| Variance |
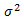
|
| Mode |
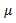
|
The normal distribution is an unbounded continuous distribution. It is sometimes called a Gaussian distribution or the bell curve. Because of its property of representing an increasing sum of small, independent errors, the normal distribution finds many, many uses in statistics. It is wrongly used in many situations. Possibly, the most important test in the fitting of analytical distributions is the elimination of the normal distribution as a possible candidate.
The normal distribution is used as an approximation for the binomial distribution when the values of n, p are in the appropriate range. The normal distribution is frequently used to represent symmetrical data, but suffers from being unbounded in both directions. If the data is known to have a lower bound, it may be better represented by suitable parameterization of the Lognormal, Weibull or Gamma distributions. If the data is known to have both upper and lower bounds, the Beta distribution can be used, although much work has been done on truncated Normal distributions.
sigma = 1; mean = 0
- Description
- Generates a sample of the normal distribution.
- Parameters
-
Name Type of value Description sigma double The shape parameter = standard deviation. mean double The shift parameter = mean value. - Result
-
Type Description double The generated sample.
- Description
- Generates a sample of the normal distribution with mean set to 0. Is equivalent to normal(sigma, 0).
- Parameters
-
Name Type of value Description sigma double The shape parameter = standard deviation. - Result
-
Type Description double The generated sample.
- Description
- Generates a sample of the normal distribution with mean set to 0 and sigma set to 1. Is equivalent to normal(1, 0).
- Result
-
Type Description double The generated sample.
- Description
- Generates a sample of the normal distribution using the specified random number generator.
- Parameters
-
Name Type of value Description sigma double The shape parameter = standard deviation. mean double The shift parameter = mean value. r java.util.Random The random number generator. - Result
-
Type Description double The generated sample.
This document includes content from the “Stat::Fit User's Manual”. Copyright 2016 Geer Mountain Software Corp.
-
How can we improve this article?
-


