AnyLogic enables users to choose any colors they like for their graphical elements. This can be done using the Color picker.
The Color picker is commonly used when the user wants to specify some Fill color or Line color for a shape or a model element.
To choose some custom color
-
Open the dialog box containing the set of most used colors by clicking inside the Fill color or Line color control.
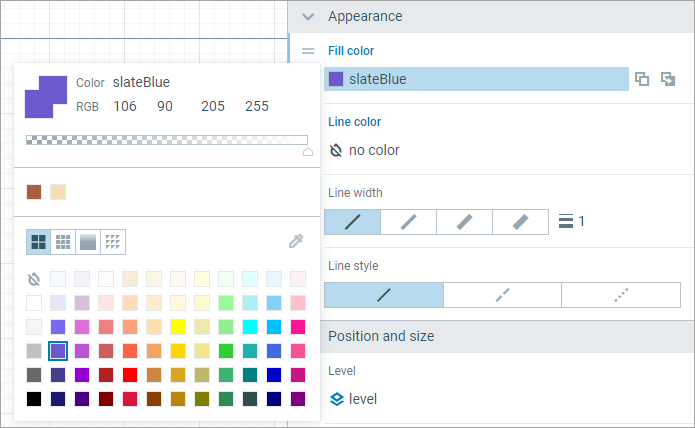
- Choose the color you like using the provided controls (they are described below).The changes apply immediately.
To set up the opacity
Opacity can be set in several ways:
- With the slider at the top of the dialog. To give you a perspective on how transparent the color is, it will be shown in the preview pane with the background of checkered gray and white boxes.

- With the far right RGB control.
- With
 No color control — if you wish to remove a color completely. Setting up the 0 for Opacity will give you the identical result.
No color control — if you wish to remove a color completely. Setting up the 0 for Opacity will give you the identical result.
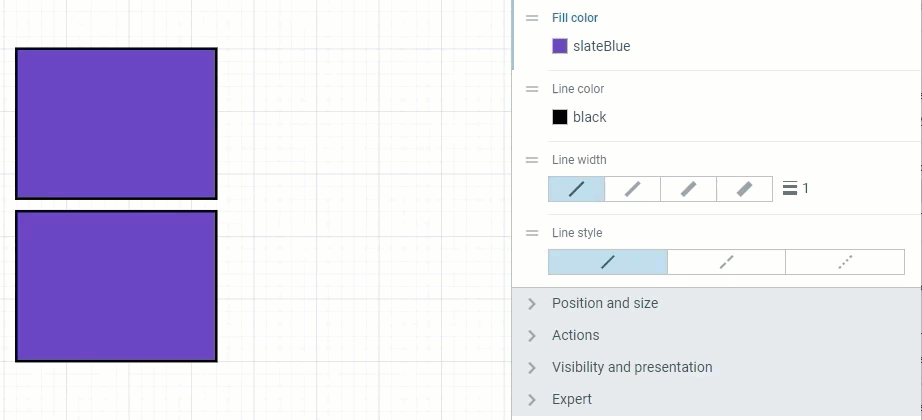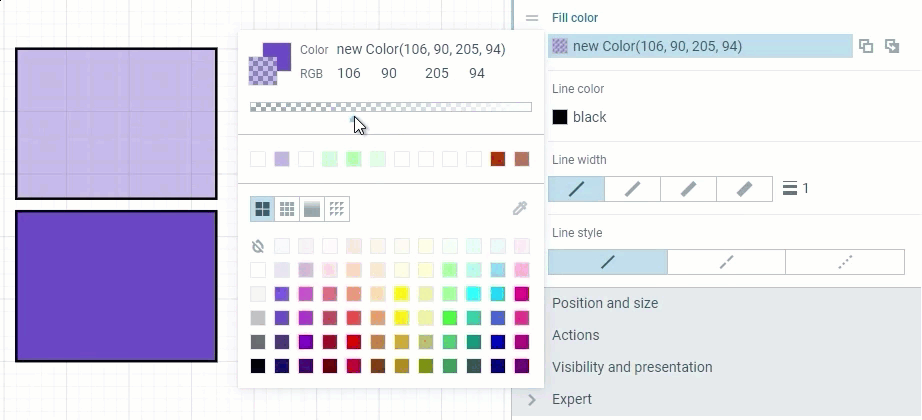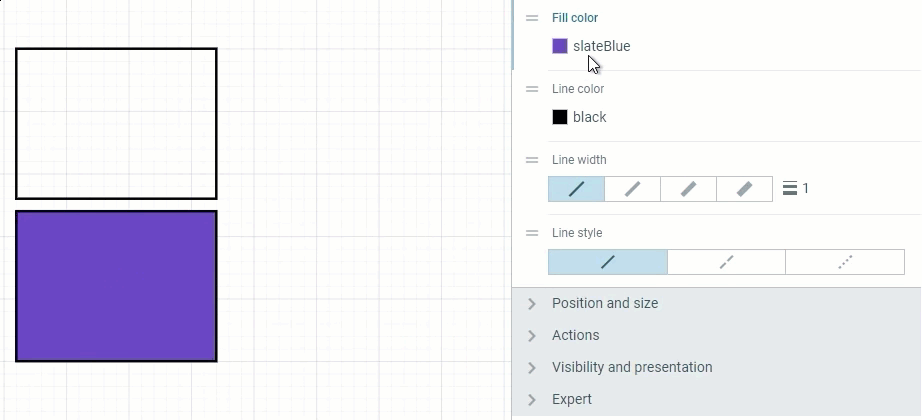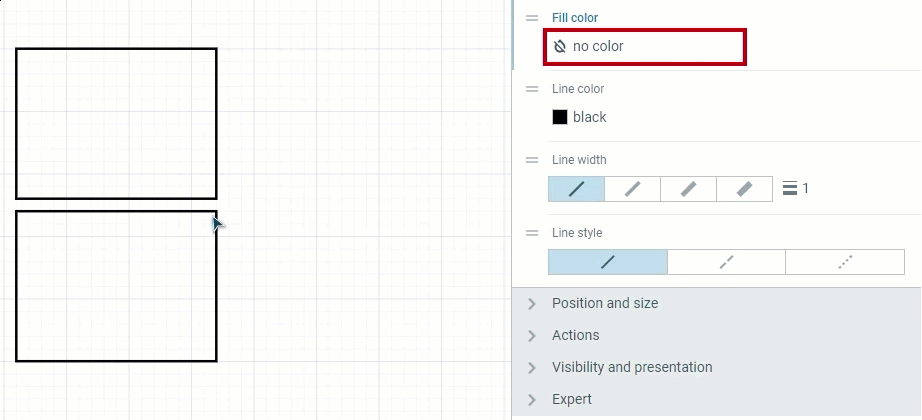 Two methods of setting a transparent Fill color
Two methods of setting a transparent Fill color
The color picker contains the following controls:

- The preview pane in the upper left corner shows the color that was initially set for the edited model element (Initial) and, in front of it, the currently selected color (Selected).
- Color — Displays the name of the chosen color, or Java expression for the custom colors.
- RGB — Displays the four controls corresponding to the currently chosen color represented by Red, Green and Blue color components followed by the current opacity value (Alpha).
- Opacity — The slider sets the opacity for the color. The opacity value is displayed in the far right RGB control (Alpha). 255 corresponds to fully opaque color, 0 — to fully transparent.
- Recent colors — Recently used custom colors are displayed below the slider.
- Four buttons to open corresponding tabs —
 Standard colors,
Standard colors,  All colors,
All colors, Spectrum and
Spectrum and  Textures.
Textures. - An
 Eye dropper — Allows to select a color from the surroundings.
Eye dropper — Allows to select a color from the surroundings. - Colors area — Contains the common colors, spectrum or textures, depending on the tab. The first element is
 No color which allows user to remove the color.
No color which allows user to remove the color.
The ![]() Eye dropper allows the user to pick a color from the surroundings. When you click onto the
Eye dropper allows the user to pick a color from the surroundings. When you click onto the ![]() Eye dropper it opens a lens, and the next click sets the color that was displayed in the lens at the moment of the click.
Eye dropper it opens a lens, and the next click sets the color that was displayed in the lens at the moment of the click.
![]() Eye dropper functionality is supported in Chrome, Edge and Opera web browsers.
Eye dropper functionality is supported in Chrome, Edge and Opera web browsers.
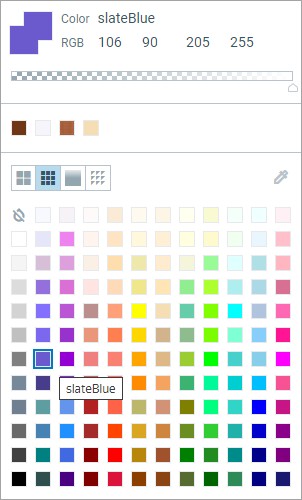
The All Colors tab allows the user to choose a color from the set of standard colors. When you hover the mouse over a color from the palette, a tooltip displaying the symbolic name of that color appears.
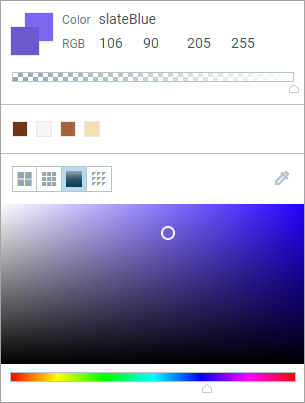
The ![]() Spectrum tab enables you to choose some custom color. You can select any color on the spectrum by dragging the handle in the Colors area. Or you can specify Red, Green, Blue and Alpha color components directly in the controls above. Alpha value defines the color opacity: 0 defines the completely transparent color, 255 defines the opaque color.
Spectrum tab enables you to choose some custom color. You can select any color on the spectrum by dragging the handle in the Colors area. Or you can specify Red, Green, Blue and Alpha color components directly in the controls above. Alpha value defines the color opacity: 0 defines the completely transparent color, 255 defines the opaque color.
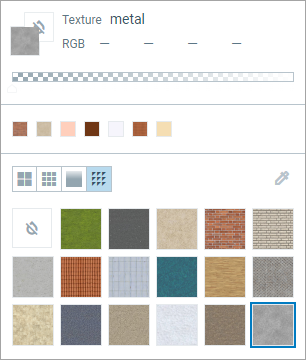
The Textures tab allows you to choose some textures for a more realistic appearance. The transparency does not apply to them. Simply select the texture to apply it.
You can set a color by specifying a valid Java expression in the color field.
Several alternative syntaxes are allowed. You can specify:
- AnyLogic color constant:
- red,
- magenta,
- dodgerBlue,
- and others, see the full list in the Color constants section.
-
Java constructor:
- new Color(int r, int g, int b) — Creates an opaque sRGB color with the specified red, green, and blue values in the range (0 - 255).
- new Color(int r, int g, int b, int a) — Creates an sRGB color with the specified red, green, blue, and alpha values in the range (0 - 255). Alpha value defines the color opacity: 0 defines the completely transparent color, 255 defines the opaque color.
-
Color component values in the following formats:
- Series of int values in the format rrr ggg bbb, each component takes values from 0 to 255. Example: 120 37 0.
- Series of float values in the format r g b, each component takes values from 0.0 to 1.0. Example: 0.5 1 0.2.
- Hex value in the formats #rrggbb and #aarrggbb, each xx component takes values from 00 to ff. Example: #00ff00 — green color.
The most popular colors are listed on the ![]() Standard colors tab or the
Standard colors tab or the ![]() All colors tab (see figure below).
All colors tab (see figure below).
In the case you want to use some other color, you can choose it on the ![]() Spectrum tab of the color picker by dragging the handle in the Colors area, or specifying Red, Green and Blue color components evidently.
Spectrum tab of the color picker by dragging the handle in the Colors area, or specifying Red, Green and Blue color components evidently.
 Set of standard colors (as shown in the All colors tab)
Set of standard colors (as shown in the All colors tab)
In the case you want to dynamically switch to some of these standard colors, you may refer to the required color using the name of the corresponding constant. The table below lists the names of color constants for all the standard colors shown above. Use indexes (A..L, 1..12) to find the correspondence between cells of these tables.
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | |
| 1 | No color | ghostWhite | cultured | snow | antiqueWhite | floralWhite | oldLace | ivory | lightGoldenRodYellow | mintCream | azure | lavenderBlush |
| 2 | white | lavender | violet | seaShell | bisque | cornsilk | papayaWhip | lightYellow | lemonChiffon | honeyDew | aliceBlue | pink |
| 3 | whiteSmoke | thistle | plum | linen | navajoWhite | paleGoldenRod | blanchedAlmond | beige | paleGreen | lightCyan | powderBlue | lightPink |
| 4 | gainsboro | mediumPurple | orchid | mistyRose | peachPuff | khaki | moccasin | lightGreen | greenYellow | paleTurquoise | lightBlue | paleVioletRed |
| 5 | lightGrey | lightSlateBlue | mediumOrchid | rosyBrown | lightSalmon | yellow | wheat | mediumAquaMarine | chartreuse | aqua | lightSteelBlue | hotPink |
| 6 | silver | mediumSlateBlue | darkOrchid | darkSalmon | coral | gold | tan | darkSeaGreen | lawnGreen | aquamarine | lightSkyBlue | deepPink |
| 7 | gray | slateBlue | darkViolet | lightCoral | salmon | orange | burlyWood | yellowGreen | lime | mediumTurquoise | skyBlue | magenta |
| 8 | lightSlateGray | darkSlateBlue | blueViolet | indianRed | bitterSweet | darkOrange | sandyBrown | mediumSeaGreen | mediumSpringGreen | darkTurquoise | deepSkyBlue | violetRed |
| 9 | slateGray | cadetBlue | cornflowerBlue | fireBrick | tomato | darkKhaki | feldspar | olive | springGreen | turquoise | blue | mediumVioletRed |
| 10 | dimGray | steelBlue | steelBlue | brown | orangeRed | goldenRod | peru | oliveDrab | limeGreen | lightSeaGreen | mediumBlue | darkMagenta |
| 11 | darkGray | teal | royalBlue | darkRed | red | darkGoldenRod | sienna | green | forestGreen | darkCyan | darkBlue | purple |
| 12 | black | darkSlateGray | indigo | maroon | crimson | espressoMartini | saddleBrown | darkOliveGreen | darkGreen | seaGreen | navy | midnightBlue |
Plus to the “classical” colors listed above, you can use any other “custom” colors. You create your color as the instance of standard Java class Color.
-
new Color( <red>, <green>, <blue> ) — creates a new color from given RGB values; each value must be in the range [0..255].
Example: rectangle.setFillColor(new Color(0, 220, 100) ); -
<color>.brighter() — creates brighter version of a given color.
Example: oval.setFillColor(red.brighter()); -
<color>.darker() — creates darker version of a given color.
Example: oval.setFillColor(red.darker());
-
new Color(<red>, <green>, <blue>, <alpha>) — creates a transparent color with the given RGB. <alpha> = 0 means totally transparent, <alpha> = 255 means totally opaque.
Example: line.setColor(new Color(0, 0, 100, 30) ); -
semiTransparent(Color color) — creates a semi-transparent version of the given color. color can be defined with a color constant, or the new Color(<red>, <green>, <blue>) constructor described above.
Example: line.setColor(semiTransparent(blue)); -
transparent(Color color, double fraction) — creates a transparent version of the given color. color can be defined with a color constant, or the new Color(<red>, <green>, <blue>) constructor described above. fraction defines the opacity ratio. It takes values in the range [0..1], 0 means transparent, 1 — opaque.
Example: line.setColor(transparent(blue, 0.7));
Assume you have several different but similar shapes in your model, which you wish to display using different colors that go well together. The function spectrumColor(int index, int period) will return an attractive color with a given index out of period different colors evenly distributed over the whole spectrum.
In the given demo model we show how to use different colors obtained using the spectrumColor() function for ten individual items of the replicated shape (examine the shape's properties: Fill color, X, Replication).

-
Set null as the color of the element’s component (fill or outline).
Example: oval.setLineColor(null);
Please see Java documentation on class Color for more information.
-
How can we improve this article?
-


