In pedestrian flow models, the services define a group of similar physical service objects (turnstiles, ticket vending machines, security checkpoints, check-in counters, and so on).
There are two types of space markup shapes that you can use to draw services in your pedestrian model:
Service with Area — Use this to define a service with an electronic queue (such as a bank teller, railway station information desk, and so on). Pedestrians do not stand in a queue line, but wait for their turn in the adjacent area. The area is defined by a polygonal node.
Service with Lines — Use this to define a service with a queue where pedestrians wait in a queue line until the service becomes available. Two types of queues are supported: standard queues lines, and a “serpentine” queue typically used in airport check-in areas.
First, you draw the service in the graphical diagram, then add the PedService Pedestrian Library block to the flowchart and configure it by tuning its parameters.
To draw a service with area
-
Drag the Service with Area
element from the
Space Markup palette to the graphical diagram. You will see the markup shapes: two services and the adjacent area.
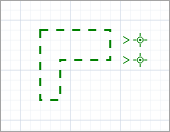
-
First, resize the area to make it match the area on the drawing of the simulated space. Select the area shapeÇ when working with markup shapes, the first click selects all shapes of this markup element (in our case — two service shapes and the area shape).
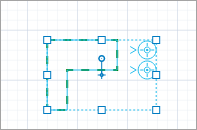
The second click selects a specific shape.
You can now edit this particular shape without affecting other markup shapes.
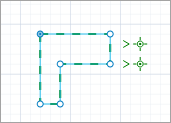
The third click on the same shape selects all shapes of that markup element.
-
You can modify the shape by dragging its points. You can add a point by double-clicking the border of the shape, and you can remove a point by double-clicking it.
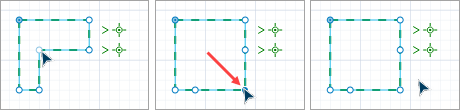
-
Locate the service points in the graphical diagram. They are usually located with the same offset. If necessary, place these two service points so that their locations match the drawing before you change the number of services. Then the service points that you add later will be located with this custom offset. To move a service point, select it and drag without releasing the left mouse button.
-
You can now change the number of service points. Open the service properties and change the value inside the Number of services control. Increase it to 4, and you will see more service points appear in the graphical diagram.
- General
-
Name — The name of the service. The name is used to identify and access the service shape from Pedestrian Library block properties.
Show name — If selected, the service name is displayed in the graphical editor.
Lock — If selected, the service is locked. Locked elements do not respond to mouse clicks, and they cannot be selected in the graphical editor until you unlock them. This is often needed when you want to prevent the element from being edited while other elements are placed over it.
Ignore — If selected, the service is excluded from the model.
Number of services — Here you can define the number of service points.
- Appearance
-
Service color — The color of service shapes.
- Position and size
-
Level — The level to which this service belongs.
- Visibility and presentation
-
Visible — If selected, the service is visible during animation at model runtime.
Show in — Select whether the shape is displayed in both 2D and 3D animation, 2D only, or 3D only.
Agent presentation — If selected, the service is also visible on the upper-level agent that hosts the agent containing this service.
You can obtain the properties of the service with area at model runtime using the API.
- Statistics
-
Function Description double getUtilization() Returns the services utilization, defined as the average utilization across all service points. The utilization of each service point is calculated as the fraction of time the service is busy - that is, when a pedestrian is being served and is directly at the service point. Time spent moving from the queue to the service point and recovery time are not counted as working time. The returned utilization value is in the range [0..1]. void resetStats() Resets the service with area utilization statistics. - Area
-
Function Description QueueArea getQueueArea() Returns the rectangular area belonging to the current service with area. List getQueues() Returns the list of areas (containing a single area) belonging to the current service with area element. - Level
-
Function Description Level getLevel() Returns the level on which this service is located. - Removal
-
Function Description void remove() Removes the service with area from the presentation. If this element is not a part of presentation, the function does nothing. Note, that removal from the presentation does not necessarily mean removing from the model logic, since logical networks and routes may have been created before the removal and survive it.
-
How can we improve this article?
-


