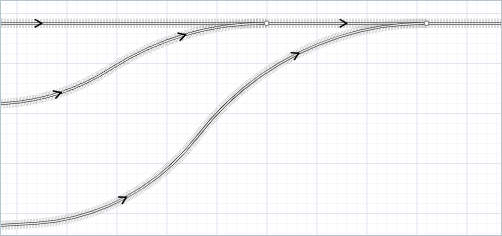
Railway Track is a graphical space markup element that represents a continuous rail track (that is, without switches) of any shape. The track can contain multiple linear and curved segments. A single track is automatically placed within a railway network, which can be further extended by adding and connecting additional tracks.
The track takes into account switches at both ends, if there are any. If there is no switch at either end (an open-ended track), and a rail car exits the track at that end, the car leaves the yard model.
The track retains information about all cars that are (partially or fully) located on it, and you can obtain those cars using the track API.
 Cars on a track
Cars on a track
To draw a railway track
-
Double-click the
 Railway Track element in the Space Markup section of the
Railway Track element in the Space Markup section of the  Rail Library palette.
Rail Library palette.
The cursor icon should turn into
. It means that the drawing mode is activated and you can now draw railway track in the graphical editor point by point.
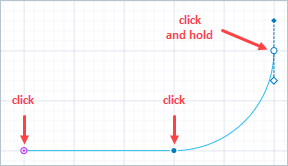
- Click in the graphical editor to draw the first point of the track. Do more clicks to add more points.
-
To draw a curved segment, do not release the mouse button while clicking, but move the mouse with the left mouse button pressed.
-
Finally, put the final point of the track with the double-click.
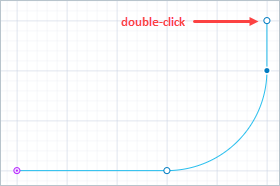
- General
-
Name — The name of the track. The name is used to identify and access the track from code and flowchart blocks’ properties.
Show name — If selected, the track’s name is displayed on the graphical diagram.
Lock — If selected, the railway track is locked. Locked shapes do not react to mouse clicks — it is impossible to select them in the graphical editor until you unlock them. It is frequently needed when you want to prevent editing this shape while drawing other shapes over it.
Ignore — If selected, the track is excluded from the model.
- Appearance
-
Track gauge — The spacing of the rails on a railway track, which is measured between the inner faces of the load-bearing rails.
- Position
-
X — X-coordinate of the track’s start point.
Y — Y-coordinate of the track’s start point.
Z — [Enabled if Show in 3D option is selected] Z-coordinate of the track’s start point.
- Points
-
The table located in the Points property section enables users to view and adjust coordinates of the track turning points.
Here you define relative coordinates, not the absolute ones. The first point always has coordinates (0, 0, 0) that cannot be changed.
Other rows of the table define relative coordinates of the successive points. Coordinates of each point are actually offsets of the corresponding point from the start point along X, Y (and optionally Z) axes correspondingly.
- Visibility and presentation
-
Visible — Here you specify whether the shape is visible on animation at model runtime, or not. Using the control, choose yes or no.
Show in — Here you can choose whether you want the shape to be shown both in 2D and 3D animation, or in 2D only, or in 3D only.
Agent presentation — If selected, the track is also visible on the upper agent where this agent lives.
To move a point of a railway track
- Select the track with a click.
- Drag the track’s point.
To add a new salient point to a track
- Double-click the track where you want to add new salient point.
To remove a point of a track
- Double-click on the track’s point you want to remove.
To add a segment to the railway track
- Right-click the track and select Append from the context menu.
- Click one of two track’s end points to indicate where you want to append new segments to the railway track.
- You are now in the drawing mode again. Draw new segments in the same way you draw the track.
- Put the final point of the railway track with the double-click.
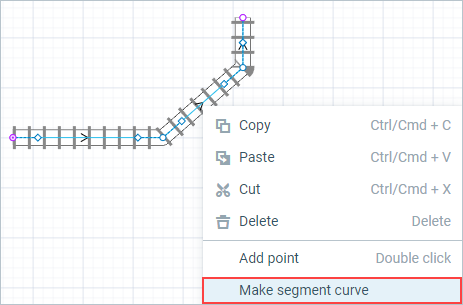
To change a linear segment into curved
- Click a railway track in the graphical editor to select it.
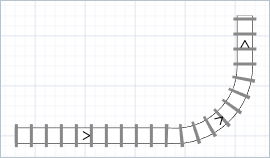
Right-click on the segment you need to change and select Make segment curve from the context menu.
Segment will appear curved.
To edit the track curvature
You can change the curvature of the track segments using guiding lines.
Right-click the track and select Show guiding lines from the context menu.
-
To modify the track curvature, drag the end of the guiding line .
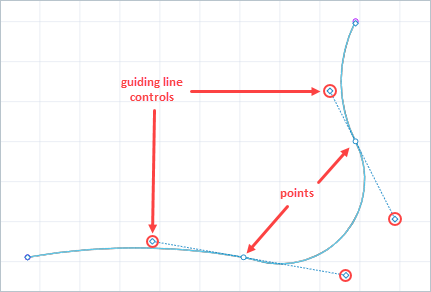
By default, when you drag a guiding line, the curvature of the both segments around the point changes. If you wish to adjust the segments of the track around the point separately, press Ctrl while dragging the end point of the guiding line.
- When you have finished editing, hide guiding lines by right-clicking the track and selecting Hide guiding lines from the context menu.
To connect two or more railway tracks into one track
Several railway tracks can be connected, with or without a railway switch.
- Drag the end point of one railway track onto the end point of another track where you want it to connect to. Two railway tracks will merge into one track.
To connect two or more railway tracks with a switch
You can connect railway tracks with a ![]() Railway switch if you draw a segment that connects anywhere to the path and not to its end point.
Railway switch if you draw a segment that connects anywhere to the path and not to its end point.
-
Connect two railway tracks at any point except the end points.
In the example below, the element railwayTrack1 was connected to railwayTrack in the middle. Multiple railway tracks can be connected this way.

The railway switch will appear in the place of connection. Now you have created a
 Railway network with several tracks in it. In the example below, the railway switch breaks the track into parts, railwayTrack and railwayTrack2, while railwayTrack1 does not merge with railwayTrack, but remains a separate track.
Railway network with several tracks in it. In the example below, the railway switch breaks the track into parts, railwayTrack and railwayTrack2, while railwayTrack1 does not merge with railwayTrack, but remains a separate track.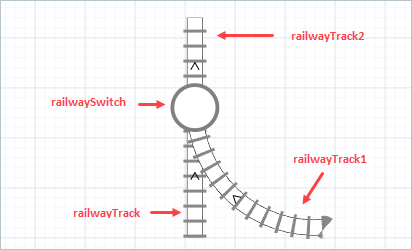
You can connect as many tracks as you need in one railway switch.
-
Click to select railway switch and edit its properties.
If you decide to delete the switch, the railway tracks will no longer be a part of the same railway network, even though they can be perceived as connected.
To split a railway track into two tracks
- Right-click the railway track and choose Split from the context menu.
- Click the track’s salient point where you want to split the shape into two individual shapes. The railway track will be split immediately even if the segments look connected in the graphical editor. You can select any of them and check that they are separate railway tracks now.
To resize the shape
- Right-click the track and choose Edit shape from the popup menu.
- You will see the selection rectangle shown. Now you can resize the shape by dragging the required rectangle’s handles.
To rotate the shape
- Right-click the track and choose Edit shape from the popup menu.
- Drag the circular handle drawn above the shape’s centre clockwise or anticlockwise.
The track has start point and end point, and therefore has orientation. The exact position on the track may be defined by the specific markup element Position on Track.
There are several arrowheads drawn on the railway track in the graphical editor, depicting the direction of the track.
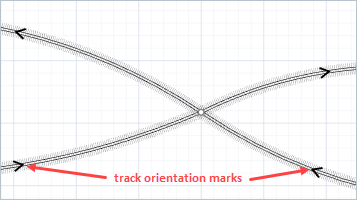
To change the direction of the track
Right-click the track in the graphical diagram and choose Change direction from the context menu or press Shift+Enter. You will notice that the arrows have changed direction.
The track API offers a range of functions to block tracks, i.e., make them unavailable for all trains, or reserve tracks, i.e., make them available only for the specified trains. The behavior of the train when the track becomes unavailable depends on the train’s state at the time of the blocking or reservation:
- The train has not started its movement yet. This track will be automatically excluded from the train’s route.
- The train is already moving. If the train has no specified route and simply follows switches, or if the route contains the unavailable track, the train will stop at the switch directly before the unavailable track and wait until it becomes available. In case you’ve set the train to calculate its route automatically, you can define the train’s behavior in the properties of the TrainMoveTo block: it can either recalculate its route to exclude the unavailable track or stop at the switch before the unavailable track and wait until it becomes available again.
- The train is moving through the blocked track. The train is allowed to leave the track but will not be able to enter it again unless the track is unblocked.
Tracks remain blocked until the unblock() function is called. The reservation is removed automatically after the specified trains have passed the track that was reserved for them, or it can be removed by calling the cancelReservation() function.
Demo model: Railway Track Reservation Open the model page in AnyLogic Cloud. There you can run the model or download it (by clicking Model source files). Demo model: Railway Track ReservationOpen the model in your AnyLogic desktop installation. Demo model: Blocking Railway Tracks Open the model page in AnyLogic Cloud. There you can run the model or download it (by clicking Model source files). Demo model: Blocking Railway TracksOpen the model in your AnyLogic desktop installation. Demo model: Level Junction Open the model page in AnyLogic Cloud. There you can run the model or download it (by clicking Model source files). Demo model: Level JunctionOpen the model in your AnyLogic desktop installation.- Cars
-
Function Description int nCars() Returns the number of cars on the track (including cars that are only partially there). Agent getFirstCar() Returns the car closest to the beginning of the track, or null if the track is empty. Agent getLastCar() Returns the car closest to the end of the track, or null if the track is empty. Agent getCar(int index) Returns a car on the track with a given index counted from the beginning of the track. All cars count: moving, standing, coupled, and cars that are only partially on this track.
index — the index of the carList<Agent> getCars() Returns the list of rail cars that are located on this track including the cars that are only partially on this track. List<Agent> getTrains() Returns the list of trains that are located on this track including the trains that are only partially on this track. boolean isEmpty() Tests if the track is empty, that is, there are no cars that are (even partially) on the track. Returns true if the track is empty, false otherwise. double getFreeSpace(boolean fromstart) Tests the availability of space on the track. If there are no cars on the track, returns infinity. If there are cars, returns the distance from the track start or end point (depending on the fromstart parameter) to the nearest car. If there is a car that has partially entered or exited the track at a given side, the functions returns a negative value.
fromstart — if true, space is checked from the start point of the track, otherwise from the end point - Switches
-
Function Description RailwaySwitch getStartSwitch() Returns switch (Switch object) at the beginning of the track. RailwaySwitch getEndSwitch() Returns switch at the end of the track. RailwaySwitch getSwitch(boolean atend) Returns the switch at the beginning or at the end of the track.
atend — if true — the switch at the end is returned, otherwise at the beginningRailwaySwitch getOtherSwitch(RailwaySwitch sw) If the given switch is a “start switch” of this track, the function returns current track’s “end switch”, otherwise it returns “source switch”. This function does not check that the given is either “start switch” or “end switch”: this is the responsibility of the user calling this function.sw — the switch (one of the track endings) - Blocks and reservations
-
Function Description void block() Blocks the track. Trains located on this track at the moment of blocking can leave the track but cannot re-enter it unless the block has been removed. void unblock() Unblocks the track. boolean isBlocked() Checks whether the track is blocked. If the function returns true, the track is blocked. If false — the track is not blocked. void setBlocked(boolean blocked) Sets the track’s “blocked” status.
blocked — if true, the track will be blocked; if false — the track will be unblocked.void reserveFor(Agent... trains) Reserves the track so that only the given trains can move through it.
trains — trains that are allowed to move through the track.List<Agent> reservations() Returns the list of trains that this track has been reserved for. void cancelReservation() Cancels existing reservations for the track. Any train will be able to move through the track provided that this track is not blocked. boolean isAvailableFor(Agent train) Checks if the given train can move through the track. The function checks for both blocking and reservation.
train — if true, the given train can move through the track; if false — the train cannot move through the track. - Location
-
Function Description RailwayNetwork getRailYard() Returns rail yard (railway network) this track belongs to, or null if it is not a part of a rail yard. - Dimensions
-
Function Description double length() Returns the length of the track in pixels. double length(LengthUnits units) Returns the length of the track in specified length units.
units — a constant defining the length unitsdouble getWidth() Returns the width of the track, measured in pixels. double getWidth(LengthUnits units) Returns the width of the track, measured in given units.
units — a constant defining the length unitsvoid setWidth(double width) Sets the width of the track, 0 means thinnest possible.
width — the new width of the track, in pixelsvoid setWidth(double width, LengthUnits units) Sets the width of the track, 0 means thinnest possible.
width — the new width of the track, measured in given units
units — a constant defining the length units - Level
-
Function Description Level getLevel() Returns the level on which this track is located. - Appearance
-
Function Description Texture getTexture() Returns the texture of the shape, if the shape has texture. Color getColor() Returns the color of the shape, or null if shape has no color or if it has texture (in this case getTexture() should be used instead). void setColor(Color color) Sets the color of the shape.
color — the new color, if null the track is not drawnvoid setColor(Paint color) Sets the texture of the shape.
color — the new color, if null the track is not drawn - Visibility
-
Function Description boolean isVisible() Returns the visibility of the track. If it returns true, the track is visible, if false — not visible. void setVisible(boolean v) Sets the visibility of the track.
v — visibility of the track. If true, track is visible, if false — not visible. - Removal
-
Function Description void remove() Removes this track from the presentation. If the track is not a part of presentation, the function does nothing. Note, that removal from the presentation does not necessarily mean removing from the model logic, since logical networks and routes may have been created before the removal and survive it.
-
How can we improve this article?
-


