Option list is an element that allows you to sort agents into a limited number of categories. It is often used to define such characteristics as gender, nationality, or marital status.
For example, you can define the agent’s marital status attribute as a MaritalStatus option list with the following elements:
- Single
- Married
- CivilUnion
- CommonLawMarriage
- Separated
- Divorced
- Widowed
To create an option list
-
In the Models view, next to the model name, click . A context menu will appear.
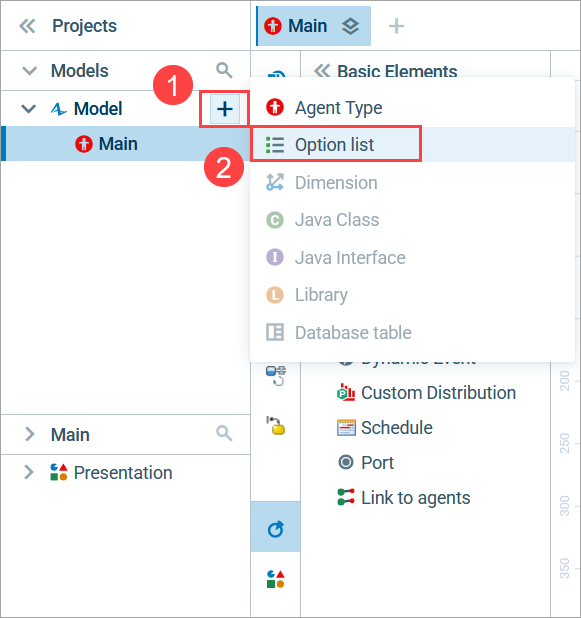
-
In the context menu, select Option list.
In the project tree, a group named Option Lists will appear. The Elements view, now titled Option Lists, will contain one element, MyOptionList. The Properties view for your option list will also be opened. - Specify the name of the element in the Properties view, under Name. In our example, the name is MaritalStatus. The name will change in the Element view.
-
In the Options list, enter the names of the options (Single, Married, and so on).
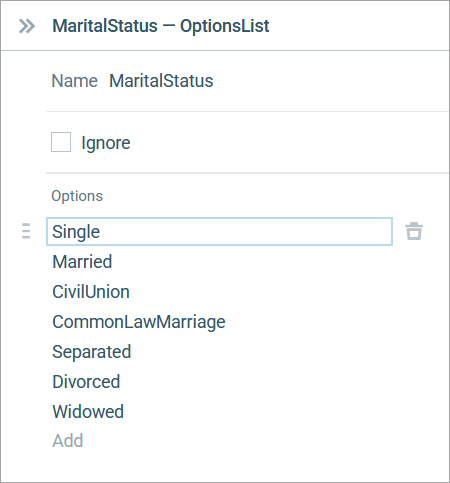
To change the order of items, drag an item using on the left. To delete an item, click on the right.
Now you can choose this list as a type or class for parameters, variables, collections and other agent attributes, and then assign the values from the option list to agents.
To specify a default value for an option list
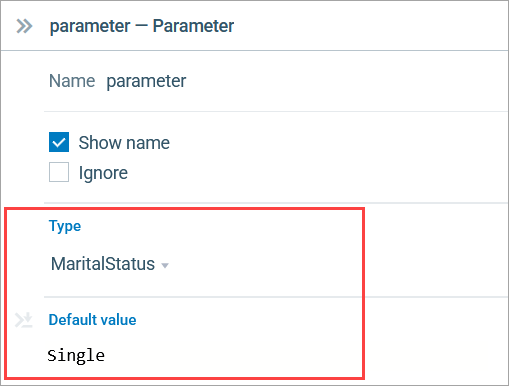
While the option list itself only stores data, you can assign different default values to different elements it is linked to. For example, a parameter representing marital status can take a default value of Single. The Parameter element itself is available in the Basic elements palette.
- In the parameter’s Properties view, open the Type drop-down list. Select the type MaritalStatus, named so after the corresponding option list.
- In the Default value field, enter Single. You can do it manually or using code completion by pressing Ctrl + Space (macOS: Fn + Ctrl + Space) while in the code box and selecting the desired option.
You can assign values to the whole agent population — for instance, you can do that in the Startup code of the top-level agent.
To randomly select one option from this option list, use one of the following functions (here we use our MaritalStatus option list as an example):
- randomFrom( MaritalStatus.class );
- MaritalStatus.random( this );
In the Java code of the model, an option list is a representation of the standard Java Enum class. It means you can use the standard Java API to interact with the option list in your code and perform basic tasks.
For example, suppose you have an option list SpeedMode with the following values: Slow, Normal, Fast.
To get all items in the option list, use the values() function:
SpeedMode[] allModes = SpeedMode.values();
After executing this code, the allModes array will be [Slow, Normal, Fast]. This is useful when you want to loop through all options or count them. Here are some examples:
-
To iterate over all items, use a simple loop on the values() array:
for (SpeedMode m : SpeedMode.values()) { traceln(m); // prints Slow, Normal, Fast } -
To count how many items there are in the list, use length:
int count = SpeedMode.values().length; // the count value is 3
For individual items of the option list, you can use additional functions:
-
To return the exact identifier of an item as it is declared in the option list, use name():
SpeedMode m = SpeedMode.Normal; String id = m.name(); // "Normal" traceln("Selected: " + id); -
To return the position of the item in the option list, use ordinal():
SpeedMode m = SpeedMode.Fast; int index = m.ordinal(); // 2 (the function is zero-based) -
To convert a string to an option list item, use valueOf():
This is particularly useful when reading data from external resources, such as files, databases, or user input, where values are stored as strings. Note that the function is case-sensitive.String speedText = "Fast"; SpeedMode m = SpeedMode.valueOf(speedText); // returns SpeedMode.Fast
For a full list of available Enum functions, see the Java 17 documentation.
-
How can we improve this article?
-


